THE 2023 JOHN MCAFEE FOUNDATION DICTUM FOR USD-PEGGED STABLECOINS

The John McAfee Foundation is proud to present and debut its first Dictum: The 2023 John McAfee Foundation Dictum for USD-Pegged Stablecoins. (Or “2023 USD-Pegged Stablecoins Dictum” for short.)
While opinions concerning cryptoinstruments vary widely and vastly in the public forum of the modern era, there is one thing that can be agreed upon by both the layman observer as well as the seasoned veteran: Their price action is [relatively] quite volatile.
This volatility serves several purposes, and in fact drives the growth of the DLT space. However, it can leave unfamiliar participants feeling quite nauseated during those precious moments spent watching price refuse to swing in their favor.
So far, the most widely adopted and simplest solution to the problem of motion sickness has been “The Stablecoin.” While not all stablecoins are pegged to the United States Dollar, the $USD’s role as the world reserve currency, as well as the numeraire used in various global markets, makes it appear a very “common-sense-by-commonality” price-target to offer the exposure-to-stability/escape-from-volatility so desperately craved by the hordes of queasy speculators.
However, the “perceived stability” offered by the US Dollar is (at this time) merely a functional extension inherent to the centralized financial system known as “fiat.” And ideologically, (at least at the time of their inception,) cryptoinstruments like Bitcoin, as well as the entirety of the early DLT industry following Bitcoin’s wake, often expressly stated intentions to exist in defiance of fiat, in spite of centralization, and in opposition to any governing authority.
(As the DLT space matures, it can seem like more and more people struggle to remember this, but you can rest assured that we at the JMF certainly aren’t in the business of forgetting it, nor passing up any opportunity to be the reminder!)
Unfortunately, the larger topic of “CENTRAL BANKS ARE DIRECTLY INCENTIVIZED TO DANGLE THE PROMISE OF CURRENCY STABILITY AS EMOTIONAL LEVERAGE ON THEIR OWN CITIZENRY, SO AS TO DOMESTICATE THEM LIKE A HERD OF HERBIVOROUS RUMINANTS INTO THE THOUGHTLESS USAGE OF, HABITUATED DEPENDENCY ON, AND NAÏVE TRUST PLACED IN THEIR PAPER NOTES VIA THE MANUFACTURED ILLUSION OF PERCEIVED NOMINAL RIGIDITY” is beyond the scope of this Dictum. But in the meanwhile, a few implementations of USD stablecoins can be addressed, and subsequently scored against a set of criteria that the JMF has determined will adequately serve as “principled goalposts” of what a USD-pegged stablecoin should strive to be, to be best aligned with the founding values of the DLT space and the inevitable and ongoing revolution it represents.
While these criteria do not encompass every possible metric of measurement, for the sake of clear and concise guidance, (for the 2023 version of this Dictum) the JMF has chosen to limit the scored criteria to the following:
- Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
- Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
- Decentralization of Management and Governance
- Transparency and Auditability
- Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation)
Before the five criteria and the reasoning for their selection is explained, one thing to mention:
A criterion that was skipped over completely and excluded was “historical price stability.” The John McAfee Foundation is not unfamiliar with the subject of currency theory. The JMF has determined it to be somewhat difficult to take “historical price stability” as a metric seriously, when the price target of 1 USD itself is subject to the whims of governments willing to debase it on a moment’s notice: Either to appease their visceral constituency or the special interest groups waiting patiently for their due reciprocation of favors. Additionally, the price charts of every currency measured herein contains deviations from their target, for a variety of underlying reasons. However, if those deviations were corrected, they were not used to disqualify or demerit any of the stablecoins listed. (USDJ and FEI are two stablecoins that ended up being excluded from this Dictum, for reasons that will be discussed later.) These reasons and events are fully excluded from analysis, but the JMF encourages inquiring minds to extrapolate their own understanding of their causality, based on how they relate to the scored criteria.
And now, an explanation of the five criteria:
Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
UST, the most well-known example of an “algostable” implementation, collapsed in 2022 for a variety of reasons. However, this does not necessarily imply that UST’s style of “algostability” is the only noncollateral-based pegging mechanism. The John McAfee Foundation acknowledges that there exist other pegging mechanisms that are not directly dependent on the existence of collateral being used to stabilize a cryptoinstrument’s price. Some of these mechanisms already exist and can be observed in the stablecoins graded in this Dictum, and others are being developed secretly, of which the JMF will omit from naming. Of the five, this criterion is weighted the most, because a stablecoin interested in achieving its purpose, while at the same time familiar with the advantages of decentralization, would ideally not rely on a single mechanism to support its peg. Therefore, any approach to the implementation of price-stability that relies too heavily on collateralization, could be in danger of “having too many eggs in one basket.” Meaning, if collateralization is a cryptoinstrument’s single safeguard, then it is likely collateralization will express itself as its single point of failure, as well. (Can you think of any examples of this?) Therefore: Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms is weighted heavier than Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms, which will be explained next.Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
In finance, there exists a concept called “time-value-of-money.” It is from the TVOM that the entire banking industry, and thus the finance industry, is able to exist, and exist profitably. (And this concept, by itself, is not inherently evil or even necessarily unethical!) Without reserves or deposits of some kind, how else could loans be offered? It is through the difference in time preference between the various actors that rely on banking services that banks maintain solvency. (Or at least this is how the current system is meant to function?) The history of banking in the United States involves eras where certain market actors known as “wildcat banks” would hyperinflate their paper banknotes without any regard to maintaining gold or silver in collateral, precipitating ridiculous financial problems from sea-to-shining-sea. Fast forward to today, and US banks are now regulated such that: their lack of gold and silver collateral is now completely permitted, and they now instead are required to maintain a reserve of an arbitrary percentage of fiat banknotes, to be held as deposits by the very central bank in charge of issuing them. Surely, at least the central bank [known as The Federal Reserve] overseeing all of this is holding precious metals or some other commodity, to collateralize the notes in circulation, right? (Don’t investigate or research this at all, thanks.)The digression of the previous paragraph was necessary to illustrate the importance of collateralization, as well as its considerations and implementations. Generally speaking, the JMF views collateralization to be an ethically responsible and morally upright endeavor. However, if said collateralization-based pegging mechanisms are in fact, relying on, and declaring the fiat notes issued by the Federal Reserve as “sound collateral,” then it seems there exists room for improvement in the overall implementation of these cryptoinstruments known as “stablecoins.” This criterion is weighted second highest, and the stablecoins ranked in this Dictum were observed to fall into one of five categories:
- Stablecoins completely-collateralized by fiat instruments. (First Degree Direct Fiat Collateralization)
- Stablecoins completely-collateralized by stablecoins completely collateralized by fiat instruments. (Second Degree Direct Fiat Collateralization)
- Stablecoins majority-collateralized by stablecoins completely-collateralized by fiat instruments. (First Degree Indirect Fiat Collateralization)
- Stablecoins minority-collateralized by stablecoins completely-collateralized by fiat instruments. (Second Degree Indirect Fiat Collateralization) Stablecoins completely-collateralized by decentralized instruments. (Decentralized Collateralization)
The first category here is scored lowest, and the fifth is scored highest.
Decentralization of Management and Governance
Humanity’s history is a story about decision making, and who ended up making the right ones. Opinions on this can vary, like opinions naturally do. However, the JMF believes that the systems established to facilitate the making of decisions, as well as the consequences of them, are just as important to view through the lens of decentralization as any other component within the DLT industry. Quite often, a system like a DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) can be implemented to decentralize the responsibility of oversight and management. However, in many cases, the DAO becomes a vehicle for the reintroduction of centralization. It is beyond the scope of this Dictum to provide too much opinion on the implementations of governance and management in DLT projects, however for the sake of being aligned with the principle of decentralization, a general rule of thumb is observed in the scoring: The less manager intercession allowed, manual involvement considered, and intrusion-by-governance required, the better the score. The JMF expects a maximum amount of outrage directed towards it from the ideologically illiterate, concerning its viewpoint in this area. (Because that’s what happens when you’re correct!)Transparency and Auditability
Generally speaking, transparency is something that should be strived towards in any endeavor that requires the building of trust with a user base. That includes unincorporated DLT projects, for-profit and non-profit corporate entities, as well as the governing institutions of nation states. The antonym of transparency is technically opaqueness, but “nontransparency” will be used contextually for clarity in communication. In this Dictum, the stablecoins are effectively scored against each other, so while all the projects maintain a degree of transparency, they will end up being ranked from most-transparent to least-transparent. If the entirety of the codebase and operating parameters are on a decentralized ledger (like a blockchain) and open-sourced, then this is an example of maximum transparency. If parts of the stablecoin operation involve centralized management methodology, then this will be considered an area of nontransparency, even with an attestation schedule. Regardless if attestations are provided on a regular periodicity, this is scored as nontransparency for all the time in between attestation reports. Additionally, if attestation is provided only by a sole auditor, then this becomes a point of centralization, and a potential single point of failure. Auditability is used here to mean “decentralized auditability.” If the auditing is a privilege reserved for only a select few, then this is another operational point of centralization, even with the best intentions of quality control and assurance.Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation
Traditionally, Capital Efficiency is defined as “the ratio of capital expenditure to revenue generated.” However, in the context of stablecoins and their collateral, Capital Efficiency is the term that encompasses the collateralization ratio needed to issue and circulate a certain amount of a stablecoin. (While beyond the scope of this Dictum, a Stablecoin Dilemma can be described between a focus on Capital Efficiency versus Decentralization of Collateral. This is also borrowed from the “Stablecoin Theory” mentioned before.) The reader might notice an observable inverse correlation: Capital Efficiency tends to be highest for stablecoins where Decentralization tends to be lowest. However, if Capital Efficiency is not taken seriously by DLT innovators, their decentralized solutions to stability will constantly get outperformed by their centralized competitors. Because they’re more Capital Efficient!Nonzero-Sum Value Creation was almost going to be separated into a sixth criterion, but it was bundled in with Capital Efficiency because it affects the same parameter, which is the [potential] net change in economic value made possible via the project’s existence, or additional utilities/use cases. Whereas Capital Efficiency can be a net decrease of economic value when more overcollateralization is required (or vice versa), Nonzero-Sum Value Creation can be a net increase of economic value if said collateralization mechanisms provide opportunity zones for actors (ideally decentralized), who are incentivized to contribute to price-stability via some kind of differentiated involvement or activity. Some stablecoins have nothing to offer besides their… stability. While there is nothing inherently wrong with this, the JMF salutes innovation, and will score stablecoins higher if their ecosystem involves a greater variety of possible economic interaction. This criterion is weighted the lightest. However, the decentralization of value creation will be scored higher than centralized or “privileged” value creation.
Depending on how rigorously you want to deduce the way this Dictum was analyzed and scored, you can assign a weight of “5” to the first criterion, descending by whole numbers to a weight of “1” for the fifth criterion.
While not every minute detail involved in scoring this Dictum will be addressed, the following sections will be subdivided by the USD stablecoin project names and symbols, with the reasoning behind their rankings in the criteria delivered with maximum brevity and conciseness. We will not be providing a complete explanation of the projects, and the reader is encouraged to do their own research. None of what is written here constitutes financial or investment advice of any kind!
Additionally, whenever two stablecoins score into a draw or a tie, they may end up “sharing the rank” for that criterion on the Dictum. For example, if two stablecoins share 1st place, then the next-highest scoring project would be listed in 3rd place. If three stablecoins share 1st place, then the next-highest scoring project would be listed in 4th place.
The JMF would also like to address that (mostly applicable to the first and third criteria) this Dictum is scored based on the quantity number of mechanisms, and their ability to be differentiated from each other, that are employed in the process of maintaining price stability/decentralization. So, the documentatoon of these projects, and the subjective way they are writen, have a significant ability to sway the scoring of the way they are judged. Early criticism of this Dictum has been focused on finding disparities between the way the criteria was scored, and how the documentatioon of the scored projects have litle “incentivized pressure” to describe their mechanisms in a way that aligns with the viewpoint of the JMF. The JMF acknowledges this imperfection in its [early] methodology! The JMF did not want to “lose the element of surprise” in its first Dictum, however it is expected that in future years, our methodology for scoring Dictums will become more objective, more clear, more quantifiable, and less subjective to the biases or misrepresentations that projects tend to contain in their documentation. Meaning, the 2024 and 2025 versions of this Dictum will be even beter than this one!
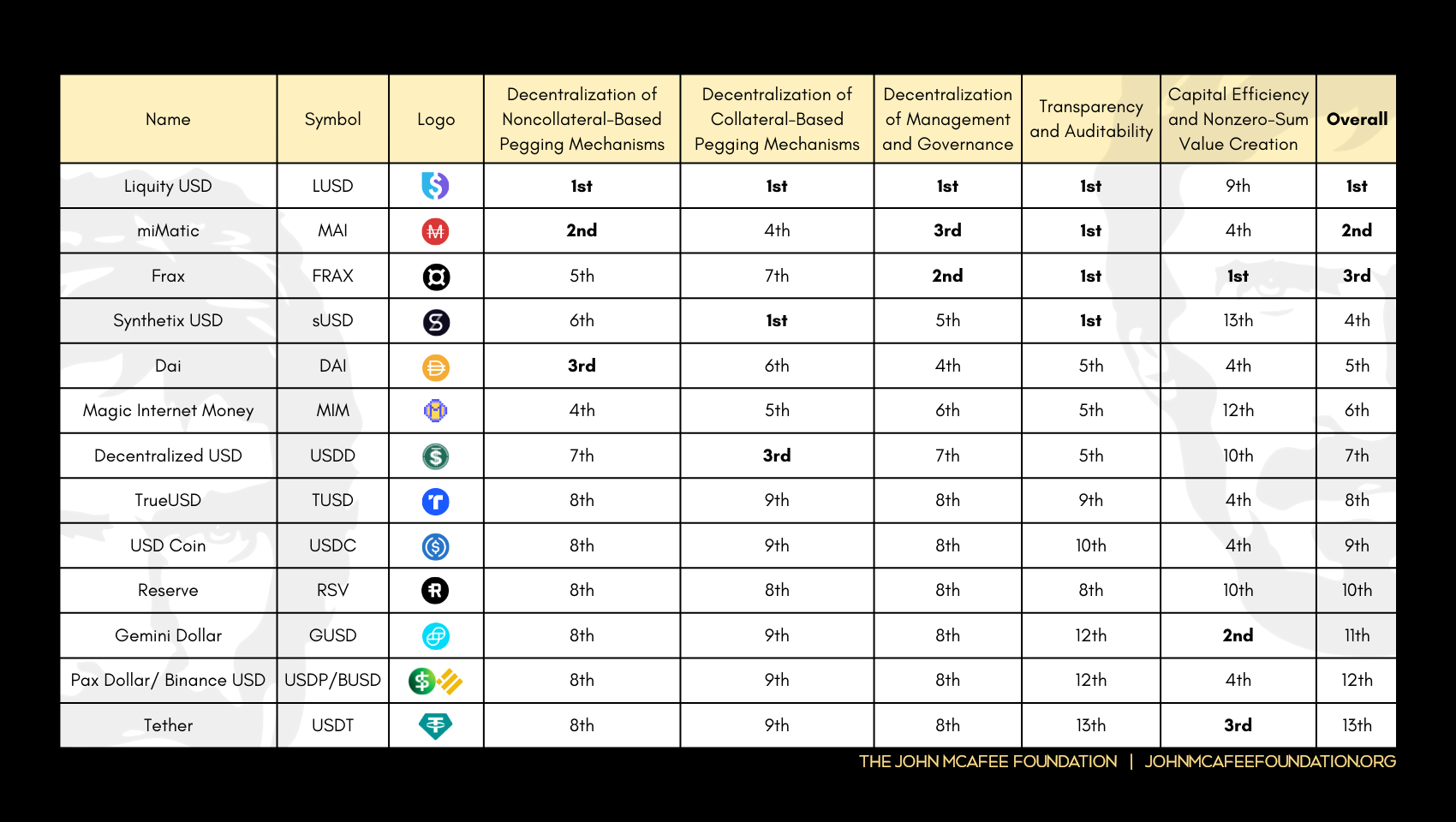
(The order of appearance of the stablecoin projects as they subsequently appear through the rest of this writing is completely arbitrary, is different than how it is listed in the associated image version of this Dictum, and is not an indication of anything remarkable.)
Results and Analysis
- Tether
- USD Coin
- TrueUSD
- Dai
- Pax Dollar - Binance USD
- Decentralized USD
- Gemini Dollar
- Magic Internet Money
- Frax
- Liquity USD
- Synthetix USD
- Reserve
- MiMatic
Tether is the oldest stablecoin, and is backed by fiat collateral. Tether arguably pioneered the concept of a stablecoin, as well. Their documentation does acknowledge the following:
“We recognize that our implementation isn’t perfectly decentralized since Tether Limited must act as a centralized custodian of reserve assets.”
“We understand that our implementation doesn’t immediately create a fully trustless cryptocurrency system.”
The John McAfee Foundation applauds Tether for admitting they know this.
However, as far as this Dictum goes, this means Tether is not leading the pack in decentralization.
Of the $67B in the December of 2022 report, about $39B was held in US Treasury Bills. If the reader is not aware, T-bills are even more enmeshed into the fiat system than Fed notes. Some of the collateral backing USDT could even be precious metals, but this seems to be less than 5%.
Other stablecoins similar to USDT in business model publish attestation reports monthly, and not quarterly. Of the stablecoins that publish attestation reports, USDT is actually the lowest-frequency of that list. So it scores the lowest.
“We recognize that our implementation isn’t perfectly decentralized since Tether Limited must act as a centralized custodian of reserve assets.”
“We understand that our implementation doesn’t immediately create a fully trustless cryptocurrency system.”
The John McAfee Foundation applauds Tether for admitting they know this.
However, as far as this Dictum goes, this means Tether is not leading the pack in decentralization.
Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
The first criterion is effectively not applicable, which placed USDT at the bottom of the stack for this criterion.Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
The second criterion is “First Degree Direct Fiat Collateralization,” which is scored lowest, and also places USDT at the bottom of the stack.Decentralization of Management and Governance
The third criterion can positively view that Tether uses a multi-sig approach for issuing USDT to “mitigate a single point of failure.” However, there are other areas that could easily constitute a “single point of failure” within Tether’s model, so the multi-sig implementation does not necessarily negate the centralization elsewhere, nor give USDT a positive net score for this criterion.Transparency and Auditability
As far as the fourth criterion goes, Tether issues quarterly attestation reports, which are provided by BDO Italia. The latest available report at the time of this Dictum’s analysis, December of 2022, acknowledges that “Tether Holdings Limited and its wholly owned subsidiaries are defendants in three ongoing civil litigation proceedings,” which is arguably a transparent move to include in the attestation. Their website includes a “Transparency” page that updates “at least once per day.” However, what the Transparency page does not include is, the breakdown of the collateral, which is better shown in the attestation report:Of the $67B in the December of 2022 report, about $39B was held in US Treasury Bills. If the reader is not aware, T-bills are even more enmeshed into the fiat system than Fed notes. Some of the collateral backing USDT could even be precious metals, but this seems to be less than 5%.
Other stablecoins similar to USDT in business model publish attestation reports monthly, and not quarterly. Of the stablecoins that publish attestation reports, USDT is actually the lowest-frequency of that list. So it scores the lowest.
Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation
As far as the fifth criterion goes: Tether does well with Capital Efficiency, due to its lack of decentralization. And it even creates nonzero-sum value, as well, since the collateral being used to back its stablecoins are being deployed in various investment vehicles. However, it does not seem this value creation is decentralized, and its score will be adjusted accordingly.| Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 8th |
| Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 9th |
| Decentralization of Management and Governance | 8th |
| Transparency and Auditability | 13th |
| Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation | 3rd |
| Overall | 13th |
The sole issuer of USDC is Circle, which is a member of Centre, along with Coinbase.
Centre is the developer of the stablecoin framework that created USDC, which is open source. (USDC scores points in transparency, here.)
USDC’s documentation makes the claim that “Customers want price-stability and the regulatory framework of existing central bank money.” An arguably true statement! However, the JMF would argue that just because an opiate addict wants the type of high that only the best quality heroin can provide, does not necessarily justify the provision of said heroin to the addict as the correct course of action, even if it’s what the customer wants.
Centre is the developer of the stablecoin framework that created USDC, which is open source. (USDC scores points in transparency, here.)
USDC’s documentation makes the claim that “Customers want price-stability and the regulatory framework of existing central bank money.” An arguably true statement! However, the JMF would argue that just because an opiate addict wants the type of high that only the best quality heroin can provide, does not necessarily justify the provision of said heroin to the addict as the correct course of action, even if it’s what the customer wants.
Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
The first criterion is not applicable to USDC, and its score will reflect that.Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
The second criterion for USDC falls into “First Degree Direct Fiat Collateralization,” which Circle provides attestation reports for. This is also the lowest score for this criterion.Decentralization of Management and Governance
Although their documentation mentions a plural amount of “issuing members,” it would seem this number is quite low. The JMF is of the opinion that, for the third criterion, USDC also appears to be quite centralized in its approach to management and governance.Transparency and Auditability
Circle’s website also includes a “Transparency” page. Its attestations are monthly, so that is scored slightly more transparent than quarterly attestation. However, this type of off-chain transparency is relatively quite low as far as the scoring of this criterion.Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation
USDC would actually score lower than USDT in Nonzero-Sum Value Creation, but the value creation for both of these is centralized, so the JMF doesn’t consider the difference to be vast enough to remark further on. It would be equal in Capital Efficiency, on the higher end, due to the collateralization ratio being 1:1, or 100%.| Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 8th |
| Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 9th |
| Decentralization of Management and Governance | 8th |
| Transparency and Auditability | 10th |
| Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation | 4rd |
| Overall | 9th |
The first two things you can read if you visit the website for TUSD is:
“Money built for the new global financial system.”
“The first regulated stablecoin fully backed by the US Dollar.”
The JMF is of the opinion that these two statements must have been chosen from TUSD’s marketing department, and not anyone remotely familiar with the concept of decentralization.
The website does not specify much else! Although the documentation linked credits an entity called TrueCoin LLC being involved in its origination.
It is apparently also legal tender in the Caribbean country of Dominica.
However, they store their USD collateral in the United States, Hong Kong, and the Bahamas. Perhaps this was done to count towards some kind of decentralization? (For clarity: Extending the USD’s dominance as world reserve currency and numeraire does not score any points in decentralization.)
While mentioning that the collateral consists of “USD cash, cash equivalents and short-term, highly liquid investments of sufficient credit quality that are readily convertible to known amounts of cash” the attestation does not break down these quantities, and only lists totals.
However, the LedgerLens system does seem to generate an attestation report in real-time when requested by the user, which is of a significantly higher frequency than other stablecoin projects using a similar model.
Therefore, it scores higher than the other attestation-based collateral systems that are only posted monthly or quarterly.
In the attestation: “The Hong Kong depository institution also invests in other instruments to generate yield.” Value creation is acknowledged to exist, but it is centralized.
“Money built for the new global financial system.”
“The first regulated stablecoin fully backed by the US Dollar.”
The JMF is of the opinion that these two statements must have been chosen from TUSD’s marketing department, and not anyone remotely familiar with the concept of decentralization.
The website does not specify much else! Although the documentation linked credits an entity called TrueCoin LLC being involved in its origination.
It is apparently also legal tender in the Caribbean country of Dominica.
Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
The first criterion is not applicable, placing TUSD at the bottom of the stack.Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
The second criterion is: First Degree Direct Fiat Collateralization. This is also the lowest score.Decentralization of Management and Governance
TUSD also scores lowest on decentralization of governance and management. The JMF is of the opinion that this is not even remotely a principle involved in TUSD’s implementation. In contrast, other fiat-backed stablecoins do at least acknowledge in their documentation their lack of decentralization.Transparency and Auditability
TUSD uses “LedgerLens Real Time Reserves” as its attestation provider. Originally, it used an accounting firm called Cohen _BODY_ Co., then later it switched to Armanino LLP. It has now used The Network Firm as its auditor since 2023. The JMF is of the opinion it might be worth mentioning that The Network Firm was spun out of Armanino earlier in 2023, meaning this system of providing transparency is a relatively new endeavor.However, they store their USD collateral in the United States, Hong Kong, and the Bahamas. Perhaps this was done to count towards some kind of decentralization? (For clarity: Extending the USD’s dominance as world reserve currency and numeraire does not score any points in decentralization.)
While mentioning that the collateral consists of “USD cash, cash equivalents and short-term, highly liquid investments of sufficient credit quality that are readily convertible to known amounts of cash” the attestation does not break down these quantities, and only lists totals.
However, the LedgerLens system does seem to generate an attestation report in real-time when requested by the user, which is of a significantly higher frequency than other stablecoin projects using a similar model.
Therefore, it scores higher than the other attestation-based collateral systems that are only posted monthly or quarterly.
Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation
TUSD’s collateralization ratio is 100%, so its capital efficiency is relatively high.In the attestation: “The Hong Kong depository institution also invests in other instruments to generate yield.” Value creation is acknowledged to exist, but it is centralized.
| Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 8th |
| Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 9th |
| Decentralization of Management and Governance | 8th |
| Transparency and Auditability | 9th |
| Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation | 4th |
| Overall | 8th |
MakerDAO was one of the first decentralized autonomous organizations to launch on Ethereum. It was originally known as the Dai Stablecoin System. Initially, it accepted only ETH as collateral.
In addition to this, the DAO function itself allows MKR holders to vote on the Dai Savings Rate (DSR) which affects the peg stability indirectly. This also counts towards the first criterion.
According to daistats.com, somewhere between 25% and 45% of its collateral deposited comes from fiat-backed stablecoins, and possibly real-world assets backed by fiat, as well. If this alone was the metric, Dai would fall into a better category. However, the amount of Dai generated by those collateral sources is higher than 60%, which qualifies as a majority.
It is a function of the DAO to modify what can be accepted as collateral for DAI, and thus the accepted basket of assets changed over time.
“The Maker Protocol allows users to generate Dai by leveraging collateral assets approved by Maker Governance.”
“The project is managed by people around the world, who hold its governance token, MKR.”
“Through a system of Scientific Governance involving Executive Voting and Governance Polling, MKR holders manage the Maker Protocol and the financial risks of Dai to ensure its stability, transparency, and efficiency.”
However, the “Governance Security Module” aspect of the DAO almost implies that the DAO itself has a limited appetite for decentralization, and Dai loses some points in this criterion for this.
“The Maker Foundation plans to dissolve once MakerDAO can manage Governance completely on its own.”
Admirable!
“Every Dai in circulation is directly backed by excess collateral, meaning that the value of the collateral is higher than the value of the Dai debt, and all Dai transactions are publicly viewable on the Ethereum blockchain.”
This statement is true. Dai’s collateralization rate is roughly 186% at the time of writing this, which technically gives it lower capital efficiency than some of of the more centralized implementations, but higher than some of the more decentralized ones.
Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
Part of DAI’s pegging mechanism comes from “stability fees” charged from the issuance and redemption of DAI. Aside from stability fees, there exist collateral auctions, debt auctions, and surplus auctions which help assist DAI’s stability in a way not achieved by merely just a collateral ratio. Therefore, Dai scores very well in the first criterion.In addition to this, the DAO function itself allows MKR holders to vote on the Dai Savings Rate (DSR) which affects the peg stability indirectly. This also counts towards the first criterion.
Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
For the second criterion, however, Dai falls into the category of First Degree Indirect Fiat Collateralization. This is technically the third-best or middle score for that criterion.According to daistats.com, somewhere between 25% and 45% of its collateral deposited comes from fiat-backed stablecoins, and possibly real-world assets backed by fiat, as well. If this alone was the metric, Dai would fall into a better category. However, the amount of Dai generated by those collateral sources is higher than 60%, which qualifies as a majority.
It is a function of the DAO to modify what can be accepted as collateral for DAI, and thus the accepted basket of assets changed over time.
Decentralization of Management and Governance
Additionally, Dai’s documentation mentions the following:“The Maker Protocol allows users to generate Dai by leveraging collateral assets approved by Maker Governance.”
“The project is managed by people around the world, who hold its governance token, MKR.”
“Through a system of Scientific Governance involving Executive Voting and Governance Polling, MKR holders manage the Maker Protocol and the financial risks of Dai to ensure its stability, transparency, and efficiency.”
However, the “Governance Security Module” aspect of the DAO almost implies that the DAO itself has a limited appetite for decentralization, and Dai loses some points in this criterion for this.
“The Maker Foundation plans to dissolve once MakerDAO can manage Governance completely on its own.”
Admirable!
Transparency and Auditability
Dai is open-source! This scores it points. Dai is mostly on-chain, as well. However, some of the collateral backing DAI consists of “Real World Assets” and this causes it lose some points, compared to stablecoins which use 100% on-chain collateral.Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation
The Dai Savings Rate (DSR) allows any DAI holder to earn savings automatically and natively by locking their Dai into the DSR contract in the Maker Protocol. This counts as value creation, along with its role in the first criterion. In fact the aforementioned collateral auctions, debt auctions, and surplus auctions do as well. There also is an acknowledgement of an automated actor known as a Keeper that is incentivized via arbitrage to help the system.“Every Dai in circulation is directly backed by excess collateral, meaning that the value of the collateral is higher than the value of the Dai debt, and all Dai transactions are publicly viewable on the Ethereum blockchain.”
This statement is true. Dai’s collateralization rate is roughly 186% at the time of writing this, which technically gives it lower capital efficiency than some of of the more centralized implementations, but higher than some of the more decentralized ones.
| Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 3rd |
| Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 6th |
| Decentralization of Management and Governance | 4th |
| Transparency and Auditability | 5th |
| Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation | 4th |
| Overall | 5th |
An excerpt from their website:
“Today, Paxos issues USDP and BUSD. These two stablecoins are the safest for the following reasons:
Pax Dollar is another stablecoin that follows the First Degree Direct Fiat Collateralization model you’re likely already aware of, if you’ve read this far.
Additionally, it does not seem to be open-source, like other stablecoins in a similar model. It scores low in this criterion.
“Today, Paxos issues USDP and BUSD. These two stablecoins are the safest for the following reasons:
- They are both regulated by the NYDFS.
- They are fully backed 1:1 by cash and cash equivalents (US Treasuries with a maturity of less than 90 days and overnight loans secured only by US Treasuries).
- The reserves backing the tokens are held in fully segregated, bankruptcy remote accounts.
- The tokens are issued by an NYDFS regulated Trust company (Paxos Trust).
- Because the tokens are regulated by a primary prudential regulator, they are and always will be backed only by cash _BODY_ cash equivalents.”
Pax Dollar is another stablecoin that follows the First Degree Direct Fiat Collateralization model you’re likely already aware of, if you’ve read this far.
Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
Therefore, as far as the first criterion goes, USDP/BUSD basically score zero.Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
And we’ve already mentioned that it qualifies as First Degree Direct Fiat Collateralization, for the second criterion.Decentralization of Management and Governance
As far as the third criterion goes, Paxos aims to differentiate itself from other stablecoins in the same model, by focusing on the difference in legal structure it implements to maintain its solvency. It uses a “Trust Charter” instead of a “Money Transmitter License.” This, however, does not score it any points in decentralization.Transparency and Auditability
For the fourth criterion, Paxos publishes monthly attestation reports. The auditor is Withum for these reports. The only instruments in collateral besides cash are U.S. Treasury Bills. It can be argued that T-bills are “even more centralized” than cash.Additionally, it does not seem to be open-source, like other stablecoins in a similar model. It scores low in this criterion.
Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation
For the fifth criterion: Part of the collateral is in T-bills, which earn interest. It does not seem this interest income is decentralized in any way. Otherwise, USDP/BUSD would score well in capital efficiency, due to its lack of centralization.| Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 8th |
| Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 9th |
| Decentralization of Management and Governance | 8th |
| Transparency and Auditability | 12th |
| Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation | 4th |
| Overall | 12th |
From its documentation:
“USDD is a cryptocurrency issued by the TRON DAO Reserve with a stable price and diverse use cases.”
“USDD resolves short-term price fluctuations and cyclical price risks with its responsive monetary policy and mintage mechanism.”
This Dictum will score USDD higher in this criterion than the fiat-backed stablecoins that have absolutely nothing in this regard. However, this has to be the most centralized implementation of a decentralized noncollateral-based pegging mechanism imaginable. The JMF is of the opinion this is arguably making USDD “wrapped USDT” but somehow with less capital efficiency than 1:1?
Other noteworthy excerpts:
“Stability is maintained by the adoption of a series of monetary policies based on market conditions, relying on the TRON DAO Reserve assets.”
“The TRON network is willing to come to lead the establishment of the TRON DAO Reserve to take the first step in the development of a decentralized central bank in the industry.”
“Through buying or selling USDD and reserve assets, including TRX, BTC, USDT, and USDC on CEXs or DEX, it manages to keep USDD’s price stable.”
“Will announce each of its [open market operations] to the public to positively guide the market perception.”
(If it is not clear, all four of those excerpts score very low in decentralization.)
“On the basis of the TRX burning mechanism implemented by the USDD protocol, the TRON DAO Reserve has also introduced high-liquidity digital assets such as BTC, USDT, and TRX for overcollateralization in the protocol.”
USDD’s second criterion scores high, because it uses collateral that is 99% composed of BTC and TRX. This qualifies it to be in the second best category, Second Degree Indirect Fiat Collateralization. (It would be in the best category, with the exception of USDT being included as an ingredient in its collateralization.)
“The TRON DAO Reserve will also attract more whitelisted institutions as shareholders to better fulfill the responsibilities of the central bank.”
“TRON DAO Reserve will also act as the initial custodian to maintain the USDD authority management of TRON’s decentralized stablecoin, and guarantee it with reserve financial assets to ensure the stable exchange of USDD and the decentralization of USDD.”
“The remaining 998 billion USDD will be transferred and staked in an issue contract,” (10-day timelock smart contract). The USDD issuance process is the process of converting the TRC-10 USDD version in the authorization contract into the TRC-20 USDD version and releasing it to users.”
The JMF is of the opinion that it is not clear what the point of structuring like this is. The JMF is also of the opinion that labeling something “decentralized” does not actually count towards its decentralization, as radical as that may sound.
USDD scores low in this criterion, but not as low as the directly fiat-backed.
This is true, so USDD earns some points here. However, USDD does not score as high as other stablecoins in this criterion.
The current collateralization rate is 171% for USDD, which is a shockingly low capital efficiency for a stablecoin that is apparently assisted by an arbitrage volume containing billions of USDT.
There is not much decentralized value creation discussed clearly to mention here. USDD can be provided as liquidity, but so can all the other stablecoins, so USDD scores low in this criterion.
“USDD is a cryptocurrency issued by the TRON DAO Reserve with a stable price and diverse use cases.”
“USDD resolves short-term price fluctuations and cyclical price risks with its responsive monetary policy and mintage mechanism.”
Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
It is said to operate via algostability, but also via overcollateralization. Its minimum collateral is set at 120%. The algostability seems to be implemented from treating price deviation as an arbitrage volume against a collection of other stablecoins, comprised mostly of fiat-backed ones. (USDT as the largest one.)This Dictum will score USDD higher in this criterion than the fiat-backed stablecoins that have absolutely nothing in this regard. However, this has to be the most centralized implementation of a decentralized noncollateral-based pegging mechanism imaginable. The JMF is of the opinion this is arguably making USDD “wrapped USDT” but somehow with less capital efficiency than 1:1?
Other noteworthy excerpts:
“Stability is maintained by the adoption of a series of monetary policies based on market conditions, relying on the TRON DAO Reserve assets.”
“The TRON network is willing to come to lead the establishment of the TRON DAO Reserve to take the first step in the development of a decentralized central bank in the industry.”
“Through buying or selling USDD and reserve assets, including TRX, BTC, USDT, and USDC on CEXs or DEX, it manages to keep USDD’s price stable.”
“Will announce each of its [open market operations] to the public to positively guide the market perception.”
(If it is not clear, all four of those excerpts score very low in decentralization.)
Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
An excerpt from documentation:“On the basis of the TRX burning mechanism implemented by the USDD protocol, the TRON DAO Reserve has also introduced high-liquidity digital assets such as BTC, USDT, and TRX for overcollateralization in the protocol.”
USDD’s second criterion scores high, because it uses collateral that is 99% composed of BTC and TRX. This qualifies it to be in the second best category, Second Degree Indirect Fiat Collateralization. (It would be in the best category, with the exception of USDT being included as an ingredient in its collateralization.)
Decentralization of Management and Governance
Excerpts pertaining to governance:“The TRON DAO Reserve will also attract more whitelisted institutions as shareholders to better fulfill the responsibilities of the central bank.”
“TRON DAO Reserve will also act as the initial custodian to maintain the USDD authority management of TRON’s decentralized stablecoin, and guarantee it with reserve financial assets to ensure the stable exchange of USDD and the decentralization of USDD.”
“The remaining 998 billion USDD will be transferred and staked in an issue contract,” (10-day timelock smart contract). The USDD issuance process is the process of converting the TRC-10 USDD version in the authorization contract into the TRC-20 USDD version and releasing it to users.”
The JMF is of the opinion that it is not clear what the point of structuring like this is. The JMF is also of the opinion that labeling something “decentralized” does not actually count towards its decentralization, as radical as that may sound.
USDD scores low in this criterion, but not as low as the directly fiat-backed.
Transparency and Auditability
“All collateral assets are stored in public on-chain accounts and listed on the TRON DAO Reserve’s website for full transparency.”This is true, so USDD earns some points here. However, USDD does not score as high as other stablecoins in this criterion.
Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation
“The TRON DAO Reserve will set the USDD interest rate.”The current collateralization rate is 171% for USDD, which is a shockingly low capital efficiency for a stablecoin that is apparently assisted by an arbitrage volume containing billions of USDT.
There is not much decentralized value creation discussed clearly to mention here. USDD can be provided as liquidity, but so can all the other stablecoins, so USDD scores low in this criterion.
| Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 7th |
| Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 3rd |
| Decentralization of Management and Governance | 7th |
| Transparency and Auditability | 5th |
| Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation | 10th |
| Overall | 7th |
From the documentation:
“Each GUSD corresponds to a US dollar that is held by Gemini as one of the following types of assets:
“Combining the creditworthiness and stability of the U.S. dollar with the speed and efficiency of blockchain technology.”
GUSD is another implementation of a model you should be familiar with by now.
“As a regulated issuer, we need a technical design and implementation that gives us the ability to upgrade the Gemini dollar token so we can… pause, block, or reverse token transfers in response to a security incident or if legally obligated or compelled to do so by a court of law or other governmental body.”
“For certain high-risk actions in the Gemini dollar system, we need an offline approval mechanism.”
GUSD scores lowest in this criterion, equally to its other fiat-backed rivals.
“Proof-of-Solvency” is a series of three words that appear in their documentation, but this does not refer to anything like a blockchain consensus mechanism. The JMF is of the opinion that this was inserted by the GUSD marketing department, whose members likely felt extremely clever for inventing this term, and subsequently committing it to print.
In summary, GUSD does not score well in the fourth criterion.
“Each GUSD corresponds to a US dollar that is held by Gemini as one of the following types of assets:
- Deposits in FDIC-insured bank
- Money-market funds, invested only in US Treasury obligations
- US Treasury obligations”
“Combining the creditworthiness and stability of the U.S. dollar with the speed and efficiency of blockchain technology.”
GUSD is another implementation of a model you should be familiar with by now.
Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
GUSD scores zero here, no surprise.Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
GUSD qualifies as First Degree Direct Fiat Collateralization, for the second criterion. That is also the lowest score.Decentralization of Management and Governance
Excerpted:“As a regulated issuer, we need a technical design and implementation that gives us the ability to upgrade the Gemini dollar token so we can… pause, block, or reverse token transfers in response to a security incident or if legally obligated or compelled to do so by a court of law or other governmental body.”
“For certain high-risk actions in the Gemini dollar system, we need an offline approval mechanism.”
GUSD scores lowest in this criterion, equally to its other fiat-backed rivals.
Transparency and Auditability
GUSD has monthly attestations.“Proof-of-Solvency” is a series of three words that appear in their documentation, but this does not refer to anything like a blockchain consensus mechanism. The JMF is of the opinion that this was inserted by the GUSD marketing department, whose members likely felt extremely clever for inventing this term, and subsequently committing it to print.
In summary, GUSD does not score well in the fourth criterion.
Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation
GUSD would have a 100% collateralization ratio, which makes its capital efficiency high, or at least equal to the other centralized models. Additionally, GUSD holdings can be used to earn interest. Combining these two aspects, this is a surprisingly high score for GUSD in this criterion.Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms: 8th
Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms: 9th
Decentralization of Management and Governance: 8th
Transparency and Auditability: 12th
Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation: 2nd
Overall: 11th
MIM is a stablecoin from Abracadabra Money, which is a lending platform that uses interest-bearing tokens as collateral to borrow MIM.
Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
MIM’s stability is assisted via liquidations, liquidation fees, borrowing fees, and some arbitrage volumes created via price deviations. It scores moderately well in this criterion.Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
MIM falls into the second best category: Second Degree Indirect Fiat Collateralization. It is collateralized at least 70% by decentralized assets. However, it is the lowest-scoring stablecoin within this [second-best] category graded in this Dictum.Decentralization of Management and Governance
Certain aspects of Abracadabra Money involve decentralized management, and others not so much. There is mention of “centralized market deprecation” in the documentation. sSPELL, another token associated with Abracadabra, can be used for things like governance. However, governance has what seems to be a “guided process” involving a lot of semi-centralized approval. There is an incident mentioned in the documentation where 210B of the SPELL token was unilaterally burned by the leading developers. There is not much indication of this decision being the result of decentralized governance, so it implies this was a centralized supply-management measure. Additionally, Abracadabra Money features “Protocol-Owned Liquidity” implementations which is generally a centralized measure to give the developers’ treasury more control over their market. MIM does not score especially well in this criterion, even though it supports a significant amount of infrastructure related to it.Transparency and Auditability
MIM is 100% on-chain, so that is good for this criterion. However, it is not open-source, and seems to involve an exclusive licensing agreement, according to its repository.Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation
MIM’s collateral ratio is 271%, which does not make it especially capital efficient. However, its ecosystem does include liquidation fees, borrowing fees, interest, along with mSPELL staking that allows users to earn MIM income from the protocol revenue. Unfortunately, the combination of these two factors does not conclude with MIM scoring especially high in this criterion.| Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 4th |
| Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 5th |
| Decentralization of Management and Governance | 6th |
| Transparency and Auditability | 5th |
| Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation | 12th |
| Overall | 6th |
From its documentation:
“The world’s first fractional stablecoin and crypto native consumer price index.”
“Partially backed by collateral and partially algostable.”
“FRAX is a new type of decentralized stablecoin classifying itself as fractional-algorithmic.”
“The Collateral Investor AMO moves idle USDC collateral to select DeFi protocols that provide reliable yield.”
FRAX’s collateral is currently roughly only 21% decentralized assets, which means it is majority-collateralized by stablecoins completely collateralized by fiat instruments, which categorizes it as First Degree Indirect Fiat Collateralization. This is the third-best category in this criterion, and it scores lower here than other decentralized models.
“We eschew DAO-like active management such as MakerDAO.”
FRAX apparently does use snapshot.org, and has a “veFXS” token in its ecosystem which seems related to governance rights in some capacity. FRAX scores well in this criterion because it limits the power of its governance, which does in fact limit the DAO’s ability to corrupt itself (like some DAOs end up doing) into a vehicle of centralization. (However, the low decentralization of its collateralized assets could indicate it has not fully prevented this from occurring, but rather has incentivized centralization’s corruptive emergence differently than other models.)
Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation FRAX’s collateralization ratio was 94% at the time of recording, which gives it the highest capital efficiency of all stablecoins scored in this Dictum. Additionally, the FXS token is capable of being a value creation vehicle. There is also additional decentralized opportunities related to the aforementioned AMOs. FRAX scores the highest in this criterion.
“The world’s first fractional stablecoin and crypto native consumer price index.”
“Partially backed by collateral and partially algostable.”
“FRAX is a new type of decentralized stablecoin classifying itself as fractional-algorithmic.”
Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
FRAX uses something called an “Algorithmic Market Operations Controller” (AMO) to autonomously enact arbitrary monetary policy. Additionally, FRAX can be minted and redeemed from the system for $1 of value, allowing arbitrage to contribute to stability. Additionally, FRAX uses a secondary token, FXS, to function as its “seigniorage share.” FXS is burned as FRAX is minted, or minted as FRAX is redeemed. While this system is arguably unique and clever, FRAX does not score as high in this criterion as other stablecoins due to the lower amount of differentiated mechanisms taking place in this stability management process.Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
“While the protocol is designed to accept any type of cryptocurrency as collateral, this implementation of the Frax Protocol will mainly accept on-chain stablecoins as collateral to smoothen out volatility in the collateral so that FRAX can transition to more algorithmic ratios smoothly.”“The Collateral Investor AMO moves idle USDC collateral to select DeFi protocols that provide reliable yield.”
FRAX’s collateral is currently roughly only 21% decentralized assets, which means it is majority-collateralized by stablecoins completely collateralized by fiat instruments, which categorizes it as First Degree Indirect Fiat Collateralization. This is the third-best category in this criterion, and it scores lower here than other decentralized models.
Decentralization of Management and Governance
From the documentation:“We eschew DAO-like active management such as MakerDAO.”
FRAX apparently does use snapshot.org, and has a “veFXS” token in its ecosystem which seems related to governance rights in some capacity. FRAX scores well in this criterion because it limits the power of its governance, which does in fact limit the DAO’s ability to corrupt itself (like some DAOs end up doing) into a vehicle of centralization. (However, the low decentralization of its collateralized assets could indicate it has not fully prevented this from occurring, but rather has incentivized centralization’s corruptive emergence differently than other models.)
Transparency and Auditability
FRAX is both 100% on-chain and open source, which scores it the highest in this criterion.Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation FRAX’s collateralization ratio was 94% at the time of recording, which gives it the highest capital efficiency of all stablecoins scored in this Dictum. Additionally, the FXS token is capable of being a value creation vehicle. There is also additional decentralized opportunities related to the aforementioned AMOs. FRAX scores the highest in this criterion.
| Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 5th |
| Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 7th |
| Decentralization of Management and Governance | 2nd |
| Transparency and Auditability | 1st |
| Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation | 1st |
| Overall | 3rd |
From the first page of Liquity’s documentation:
“Liquity is a decentralized borrowing protocol that allows you to draw interest-free loans against ETH used as collateral. Loans are paid out in LUSD (a USD-pegged stablecoin) and need to maintain a minimum collateral ratio of 110%.”
“In addition to the collateral, the loans are secured by a Stability Pool containing LUSD and by fellow borrowers collectively acting as guarantors of last resort.”
Liquity as a protocol is non-custodial, immutable, and governance-free.”
Interesting!
“Stability is maintained via economically-driven user interactions and arbitrage, rather than by active governance or monetary interventions.”
“Liquity uses the current fraction of redeemed LUSD as an indicator of a peg deviation in order to autonomously set a base rate, which determines both the redemption fee and the borrowing fee.”
“The Stability Pool is the first line of defense in maintaining system solvency, stability deposits absorb and cancel the debt from the defaulted Troves.”
“Fellow borrowers collectively act as guarantors of last resort.”
“Arbitrageurs can make profits by redeeming LUSD for ETH and immediately selling the latter at a higher dollar price than the current value of the returned LUSD.”
Additionally, Liquity also has a liquidation system, and treats LUSD as being equal to USD: Parity between the two is an implied equilibrium state of the protocol.
LUSD scores the highest in this criterion. Bravo.
From its documentation:
“In practice, on-chain governance has been a difficult and heavily debated topic, with notoriously low turnouts, potentially misaligned incentives, and a high concentration of power in the hands of a few.”
LUSD scores the highest in this criterion, too.
Additionally:
“Frontend operation is provided by third parties which make the system decentralized and resistant to censorship while benefitting from growth incentives.”
“The protocol continuously issued LQTY to front-ends and depositors of LUSD in the Stability Pool.”
“In return, Stability Pool depositors are rewarded with the acquisition of collateral from liquidated positions at a significant discount.”
Liquity does have decentralized value creation, with quite a few innovative ideas in this area, but due to the high collateralization ratio, it overall scores low in the fifth criterion.
“Liquity is a decentralized borrowing protocol that allows you to draw interest-free loans against ETH used as collateral. Loans are paid out in LUSD (a USD-pegged stablecoin) and need to maintain a minimum collateral ratio of 110%.”
“In addition to the collateral, the loans are secured by a Stability Pool containing LUSD and by fellow borrowers collectively acting as guarantors of last resort.”
Liquity as a protocol is non-custodial, immutable, and governance-free.”
Interesting!
Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
From its documentation:“Stability is maintained via economically-driven user interactions and arbitrage, rather than by active governance or monetary interventions.”
“Liquity uses the current fraction of redeemed LUSD as an indicator of a peg deviation in order to autonomously set a base rate, which determines both the redemption fee and the borrowing fee.”
“The Stability Pool is the first line of defense in maintaining system solvency, stability deposits absorb and cancel the debt from the defaulted Troves.”
“Fellow borrowers collectively act as guarantors of last resort.”
“Arbitrageurs can make profits by redeeming LUSD for ETH and immediately selling the latter at a higher dollar price than the current value of the returned LUSD.”
Additionally, Liquity also has a liquidation system, and treats LUSD as being equal to USD: Parity between the two is an implied equilibrium state of the protocol.
LUSD scores the highest in this criterion. Bravo.
Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
LUSD is completely (100%) collateralized by ETH, which puts LUSD in the best category: Decentralized Collateralization. Again, bravo.Decentralization of Management and Governance
Liquity is governance-free, and designed to resist all kinds of censorship. There is no administrator that can control anything, and the deployed smart contracts are immutable.From its documentation:
“In practice, on-chain governance has been a difficult and heavily debated topic, with notoriously low turnouts, potentially misaligned incentives, and a high concentration of power in the hands of a few.”
LUSD scores the highest in this criterion, too.
Transparency and Auditability
Liquity is open-source and 100% on-chain, so it also scores the highest in this criterion.Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation
LUSD’s collateralization ratio was 271% at the time of recording this Dictum. This does not make for an especially high capital efficiency, even though Liquity’s documentation states that the minimum collateralization ratio is only 110%.Additionally:
“Frontend operation is provided by third parties which make the system decentralized and resistant to censorship while benefitting from growth incentives.”
“The protocol continuously issued LQTY to front-ends and depositors of LUSD in the Stability Pool.”
“In return, Stability Pool depositors are rewarded with the acquisition of collateral from liquidated positions at a significant discount.”
Liquity does have decentralized value creation, with quite a few innovative ideas in this area, but due to the high collateralization ratio, it overall scores low in the fifth criterion.
| Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 1st |
| Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 1st |
| Decentralization of Management and Governance | 1st |
| Transparency and Auditability | 1st |
| Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation | 9th |
| Overall | 1st |
From their website:
“Synthetix is a new financial primitive enabling the creation of synthetic assets, offering unique derivatives and exposure to real-world assets on the blockchain.”
For the purpose of this Dictum, we will be taking a look at sUSD, Synthetix’s version of a synthetic USD, that operates as a stablecoin.
sUSD is minted when SNX, Synthetix’s governance token is staked in collateral for it.
From their documentation:
“SNX stakers are incentivized to maintain their C-Ratio at the target rate.” This incentivization seems to be implemented by preventing the staker from claiming fees until they restore their ratio.
“They adjust their ratio by either minting Synths if their ratio is above the target C-Ratio or burning Synths if their ratio is below the target C-Ratio.”
“Once a staker’s C-Ratio goes below the liquidation ratio, they are eligible to be flagged for liquidation.”
“Users who flag SNX and liquidate accounts for liquidation are rewarded.”
These systems do get points for being decentralized, but they do lack in variety and sophistication, so while sUSD does qualify for having a score in this criterion, it lags a bit behind some of its contemporaries.
Additionally, from the documentation of Thales, which is a project adjacent to Synthetix:
“sUSD, an ERC-20 token, is the only truly decentralized stablecoin that has demonstrated an ability to hold a peg against other popular stablecoins including USDC, USDT, and DAI, primarily thanks to the Curve pools.” Curve Pools, for those who don’t know, use a significant majority of centralized stablecoins. This does not score sUSD any points in decentralization.
“All Synths are backed by SNX tokens.” Well that’s great news! For this criterion, sUSD qualifies for the best category: Decentralized Collateralization.
Additionally, Synthetix does use a DAO, and it has a system of Councils: Spartan Council, Grants Council, Ambassador Council, and the Treasury Council are all mentioned on their website. While a system like this probably has advantages in administrative efficiency, it does not necessarily score the highest in this criterion.
Governance also controls the C-Ratio.
Regardless, this does mean that sUSD scores highest in this criterion.
Unfortunately, 500%, or even 400%, places sUSD in the dead-last position as far as capital efficiency goes.
As far as decentralized value creation opportunities, there exist liquidation penalties, as well as inflationary SNX emissions for collateralization incentives. There are arguably other forms of value creation as well, but due to the high collateralization ratio, sUSD’s score in this criterion does not improve by mentioning more of them. The JMF again encourages the reader to conduct their own research and inquiry.
“Synthetix is a new financial primitive enabling the creation of synthetic assets, offering unique derivatives and exposure to real-world assets on the blockchain.”
For the purpose of this Dictum, we will be taking a look at sUSD, Synthetix’s version of a synthetic USD, that operates as a stablecoin.
sUSD is minted when SNX, Synthetix’s governance token is staked in collateral for it.
Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
(Within Synthetix’s own documentation, it admits parts of its system are “semi-centralized.”)From their documentation:
“SNX stakers are incentivized to maintain their C-Ratio at the target rate.” This incentivization seems to be implemented by preventing the staker from claiming fees until they restore their ratio.
“They adjust their ratio by either minting Synths if their ratio is above the target C-Ratio or burning Synths if their ratio is below the target C-Ratio.”
“Once a staker’s C-Ratio goes below the liquidation ratio, they are eligible to be flagged for liquidation.”
“Users who flag SNX and liquidate accounts for liquidation are rewarded.”
These systems do get points for being decentralized, but they do lack in variety and sophistication, so while sUSD does qualify for having a score in this criterion, it lags a bit behind some of its contemporaries.
Additionally, from the documentation of Thales, which is a project adjacent to Synthetix:
“sUSD, an ERC-20 token, is the only truly decentralized stablecoin that has demonstrated an ability to hold a peg against other popular stablecoins including USDC, USDT, and DAI, primarily thanks to the Curve pools.” Curve Pools, for those who don’t know, use a significant majority of centralized stablecoins. This does not score sUSD any points in decentralization.
Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
From its documentation:“All Synths are backed by SNX tokens.” Well that’s great news! For this criterion, sUSD qualifies for the best category: Decentralized Collateralization.
Decentralization of Management and Governance
To reiterate, Synthetix’s documentation acknowledges that it’s semi-centralized. “One example of centralization is the use of proxy contracts across much of the architecture.”Additionally, Synthetix does use a DAO, and it has a system of Councils: Spartan Council, Grants Council, Ambassador Council, and the Treasury Council are all mentioned on their website. While a system like this probably has advantages in administrative efficiency, it does not necessarily score the highest in this criterion.
Governance also controls the C-Ratio.
Transparency and Auditability
sUSD is 100% on-chain, and is claimed to be open-source. (More by the documentation of Thales than by Synthetix.)Regardless, this does mean that sUSD scores highest in this criterion.
Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation
The current collateralization ratio according to the documentation is 500%. Elsewhere, it is mentioned that it has been in the past between 400% and 700%.Unfortunately, 500%, or even 400%, places sUSD in the dead-last position as far as capital efficiency goes.
As far as decentralized value creation opportunities, there exist liquidation penalties, as well as inflationary SNX emissions for collateralization incentives. There are arguably other forms of value creation as well, but due to the high collateralization ratio, sUSD’s score in this criterion does not improve by mentioning more of them. The JMF again encourages the reader to conduct their own research and inquiry.
| Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 6th |
| Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 1st |
| Decentralization of Management and Governance | 5th |
| Transparency and Auditability | 1st |
| Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation | 13th |
| Overall | 4th |
Reserve is a project that involves its own mobile app for the facilitation of payments in local currencies.
From their documentation:
“We’ve created a digital currency, the Reserve Dollar (RSV), that maintains 1-to-1 parity with the US dollar (highly stable relative to the Venezuelan Bolívar), and a mobile app that makes it easy to store money in RSV, get paid in RSV, and pay for things with RSV (either at the thousands of merchants that now accept RSV, or by converting RSV into bolívares within seconds). Essentially we extended the stability of the US dollar to those who faced hyperinflation in Venezuela in recent years, and we are expanding to other countries in Latin America where inflation continues to be a pressing issue.”
So, Reserve is arguably a financial services application that extends the coverage of the United States Dollar into countries where the local currency is worse. While this endeavor seems to have some type of humanitarian motivation behind it, at this time and stage of development, it de facto just extends the coverage and influence of centralized fiat currency. (But instead of their local currency, “a better managed” fiat currency, perhaps with “world reserve” status.)
The JMF is of the opinion that undertakings like this are normally the CIA’s job, no? Were they not available, or something?
This is the second-lowest scoring category in this criterion. RSV is the only stablecoin in this Dictum that falls into this category. Arguably, RSV could be collateralized by things other than USDC in the future. But that is not the current collateral situation.
It also acknowledges that it is possible for the Owner to get access to the Vault funds. Apparently the Slow Wallet is under the “discretionary control of the Reserve Team.”
“We as a company will cease to have control” is also a declared statement worth acknowledging here.
RSV, at this time, does not score highly in this criterion, but perhaps they will in subsequent years.
From their documentation:
“We’ve created a digital currency, the Reserve Dollar (RSV), that maintains 1-to-1 parity with the US dollar (highly stable relative to the Venezuelan Bolívar), and a mobile app that makes it easy to store money in RSV, get paid in RSV, and pay for things with RSV (either at the thousands of merchants that now accept RSV, or by converting RSV into bolívares within seconds). Essentially we extended the stability of the US dollar to those who faced hyperinflation in Venezuela in recent years, and we are expanding to other countries in Latin America where inflation continues to be a pressing issue.”
So, Reserve is arguably a financial services application that extends the coverage of the United States Dollar into countries where the local currency is worse. While this endeavor seems to have some type of humanitarian motivation behind it, at this time and stage of development, it de facto just extends the coverage and influence of centralized fiat currency. (But instead of their local currency, “a better managed” fiat currency, perhaps with “world reserve” status.)
The JMF is of the opinion that undertakings like this are normally the CIA’s job, no? Were they not available, or something?
Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
Reserve does not seem to have anything for this criterion, so it scores in the bottom tier.Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
According to the documentation, RSV is fully comprised of USDC. In turn, USDC is fully collateralized by fiat. Therefore, the category RSV falls into is Second Degree Direct Fiat Collateralization.This is the second-lowest scoring category in this criterion. RSV is the only stablecoin in this Dictum that falls into this category. Arguably, RSV could be collateralized by things other than USDC in the future. But that is not the current collateral situation.
Decentralization of Management and Governance
Reserve’s documentation also mentions some of the infrastructure involved in governance and management, specifically the “Pauser,” the “Short Freezer,” the “Long Freezer,” and the “Guardian.”It also acknowledges that it is possible for the Owner to get access to the Vault funds. Apparently the Slow Wallet is under the “discretionary control of the Reserve Team.”
“We as a company will cease to have control” is also a declared statement worth acknowledging here.
RSV, at this time, does not score highly in this criterion, but perhaps they will in subsequent years.
Transparency and Auditability
RSV is fully comprised of USDC, but technically it’s fully on-chain besides this, so that helps it in this criterion. Reserve is also not yet a finished suite of products, so it is not open source, and it loses points here. RSV scores slightly higher in this criterion than the centralized stablecoins.Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation
RSV’s capital efficiency is high, due to it having a collateralization ratio of 100%. However, there is really nothing that can be mentioned as far as measurable value creation. (Unless you want to count facilitating the USD-based black market economy inside Venezuela? Unfortunately, that type of value creation is hard to quantify for the purpose of this Dictum.) It lags even behind the centralized stablecoins that have exposure to low-risk instruments, because RSV itself is not sharing in the yield that USDC itself generates from T-bills. RSV scores the lowest in decentralized value creation, but does not score the lowest overall in this criterion, due to the fact that it is heavily leaning on centralized collateral to compensate with a high capital efficiency.| Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 8th |
| Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 8th |
| Decentralization of Management and Governance | 8th |
| Transparency and Auditability | 8th |
| Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation | 10th |
| Overall | 10th |
From its documentation and website:
“Mai Finance is the frontend/dashboard for the QiDAO Protocol: it allows users to connect to the QiDAO Protocol via a website.”
“QiDAO is an overcollateralized stablecoin protocol. Mint MAI against the value of decentralized token collaterals.”
MAI scores very high in this criterion, due to the variety of mechanisms involved in maintaining stability, as well as the variety of actors incentivized to participate in the stabilization process.
For nonzero-sum value creation, MAI also does well: Actors are incentivized to initiate liquidations, both full and partial, by paying 50% of the vault’s debt, in return receiving a portion of the vault’s collateral. Additionally, there are airdrop rewards used to incentivize borrowing. Performance fees, liquidation fees, and interest fees, are other features that indicate the creation of value by MAI.
Between these two aspects, MAI scores fairly well in this criterion, especially considering its level of decentralization.
“Mai Finance is the frontend/dashboard for the QiDAO Protocol: it allows users to connect to the QiDAO Protocol via a website.”
“QiDAO is an overcollateralized stablecoin protocol. Mint MAI against the value of decentralized token collaterals.”
Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
MAI’s ecosystem involves features such as repayment fees, partial liquidations, interest fees, performance fees, along with other “organic market incentives and penalties.”MAI scores very high in this criterion, due to the variety of mechanisms involved in maintaining stability, as well as the variety of actors incentivized to participate in the stabilization process.
Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms
MAI’s collateral is also very decentralized. Roughly 75% of the tokens involved in collateralizing MAI are not supported by fiat in any capacity. (By another version of this Dictum’s analysis, only between 18% and 30% of the collateral backing MAI is centralized, which averages at around the same ratio.) This places MAI in the “Second Degree Indirect Fiat Collateralization” category. It is a relatively good score.Decentralization of Management and Governance
MAI is governed by QiDAO. Governance mechanisms like snapshot.org are also implemented. There are also operational limitations placed on a single liquidity provider holding too much influence, which helps MAI score highly in this criterion. MAI also uses a diverse basket of collaterals, which helps insulate it from the emergence of political factions aligned with any type of collateral-favoritism.Transparency and Auditability
MAI is open source, and 100% on-chain. This avails it the highest score in this criterion.Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation
MAI’s collateralization ratio was 199% at the time of being analyzed for this Dictum. For a highly decentralized project, this is arguably a decent score of capital efficiency.For nonzero-sum value creation, MAI also does well: Actors are incentivized to initiate liquidations, both full and partial, by paying 50% of the vault’s debt, in return receiving a portion of the vault’s collateral. Additionally, there are airdrop rewards used to incentivize borrowing. Performance fees, liquidation fees, and interest fees, are other features that indicate the creation of value by MAI.
Between these two aspects, MAI scores fairly well in this criterion, especially considering its level of decentralization.
| Decentralization of Noncollateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 2nd |
| Decentralization of Collateral-Based Pegging Mechanisms | 4th |
| Decentralization of Management and Governance | 3rd |
| Transparency and Auditability | 1st |
| Capital Efficiency and Nonzero-Sum Value Creation | 4th |
| Overall | 2nd |
The 2023 John McAfee Foundation Dictum for USD-Pegged Stablecoins is now concluded. This text was first made available to the public on johnmcafeefoundation.org, and the John McAfee Foundation reserves the right to supplement it with additional information in the future at their own discretion.
The standings and final scores in this Dictum are not likely to be changed. Rather, if any stablecoin in this Dictum seeks to improve their score or standing, they can now do so ahead of the 2024 version of this Dictum.
If anything on this Dictum was scored erroneously, the projects in question can remedy this error by updating and expanding their public-facing information ahead of the JMF’s analysis for the 2024 Dictum concerning this same topic.
Subsequent versions of this Dictum in the coming years can also include additional stablecoins, or omit stablecoins included in 2023’s.
Image versions of the Dictum were first made publicly available on the JMF’s official social media platforms.
Other things to mention in conclusion:
USDJ was excluded from this Dictum since it has been over 10% away from its claimed $1 peg for over 90 days, and it is not clear if this is an indication of permanent malfunction.
FEI was excluded from this Dictum since it is not clear what state the project is in, and this could also be an indication of permanent malfunction.
The stablecoins analyzed in this Dictum qualified for selection via a combination of metrics, that included market capitalization, clarity of documentation, perceived functionality, along with other miscellaneous parameters.
We hope you have enjoyed this Dictum, but understand your enjoyment was not numbered among the JMF’s purposes in conducting and/or publishing it.
More Dictums will be published by The John McAfee Foundation soon!
Topics to [likely] include:
- Worst Countries To Use The Internet In
- Most Unsecure Programming Languages
- Best Encrypted Messaging Applications
- Best Browser Extension Wallets
- Best Tax Havens
- Most Unsecure Payment Processors
- Most Invasive Mobile Phone Models
And many more! The list of Dictums above is not meant to indicate a sequence of milestones, nor a comprehensive and complete sequence, and may be published in an order different from shown.
SHARE THIS POST
SIGN UP TO RECEIVE UPDATES FROM THE JOHN MCAFEE FOUNDATION
By submitting your name and email address, you agree to receive news, updates and information directly from The John McAfee Foundation to your inbox. The JMF will never share your name or email address with any thrid party without your prior consent.

